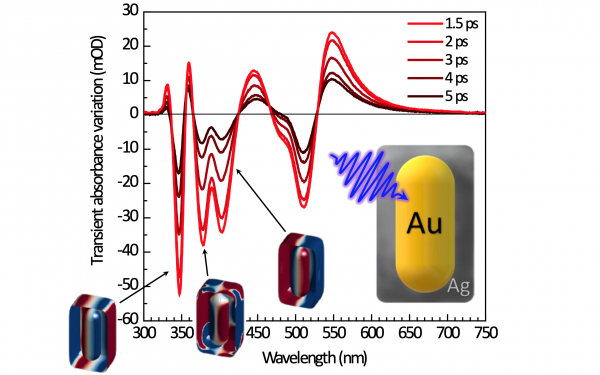
Noble metal nanoparticles exhibit localized plasmon resonance modes that span the visible and near-infrared spectral ranges and have many applications. Modifying the size, shape, and composition of the nanoparticles changes the number of modes and their properties. The characteristics of these modes are transiently affected when illuminating the nano-objects with ultrashort laser pulses. Here, we synthesize core- shell gold-silver nanocuboids and measure their spectral signature in the stationary and ultrafast transient regimes. Their dipolar transverse mode vanishes with increasing Ag-shell thickness, while higher-order modes grow in the near-ultraviolet range where no plasmon resonance can be generated with single noble metal nanoparticles. These higher-energy modes are associated with sharp spectral variations of the ultrafast transient light extinction by the bimetallic nanocuboids. By carrying out a theoretical investigation, we break down the different contributions to this response and provide a physical interpretation of its spectral profile. The transient optical signal is then shown to reveal resonance modes which are hidden in the stationary regime spectra.
Ultrafast Transient Light Extinction by Bimetallic Nanoparticles
The EFSL research group, in collaboration with the Light, Matter and Interfaces Laboratory of Université Paris-Saclay (France), has published a paper in the Advanced Optical Materials journal. The title of the article is "Sharp Spectral Variations of the Ultrafast Transient Light Extinction by Bimetallic Nanoparticles in the Near-UV" by Tadele Orbula Otomalo, Lorenzo Di Mario, Cyrille Hamon, Doru Constantin, Khanh-Van Do, Patrick O'Keeffe, Daniele Catone, Alessandra Paladini and Bruno Palpant.
https://doi.org/10.1002/adom.202001778