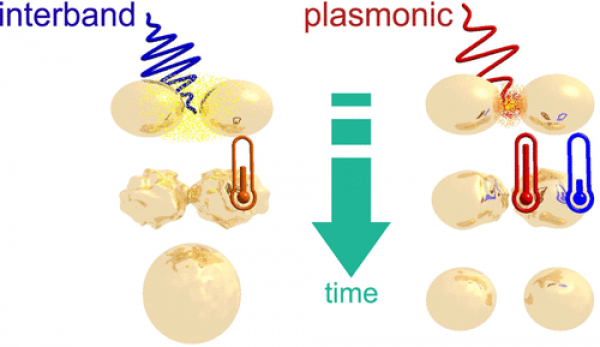
The EFSL research group, in collaboration with CNR-SPIN and University of Genoa has published a study in the Journal of Physical Chemistry C on the efficiency of ultrafast melting of gold nanoparticles upon either interband (5d →6sp) or plasmonic excitation. Interestingly the interband excitation turns out to be more efficient than plasmonic excitation for melting of the particles suggesting not all the energy absorbed by the plasmonic absorption is turned into heat. These results will have consequences both of thermoplasmonics and photocatalysis.
"Interband Transitions Are More Efficient Than Plasmonic Excitation in the Ultrafast Melting of Electromagnetically Coupled Au Nanoparticles", by Michele Magnozzi, Remo Proietti Zaccaria, Daniele Catone, Patrick O’Keeffe, Alessandra Paladini, Francesco Toschi, Alessandro Alabastri, Maurizio Canepa and Francesco Bisio.